Table of contents
Introduction
In the world of software architecture, microservices have gained significant popularity as a way to build scalable and modular systems. Microservices architecture involves breaking down a large application into smaller, loosely coupled services that can be developed, deployed and maintained independently. While microservices offer numerous benefits, implementing them effectively requires careful consideration and planning. In this article, we'll explore the best practices for implementing microservices and discuss whether it's worth the effort.
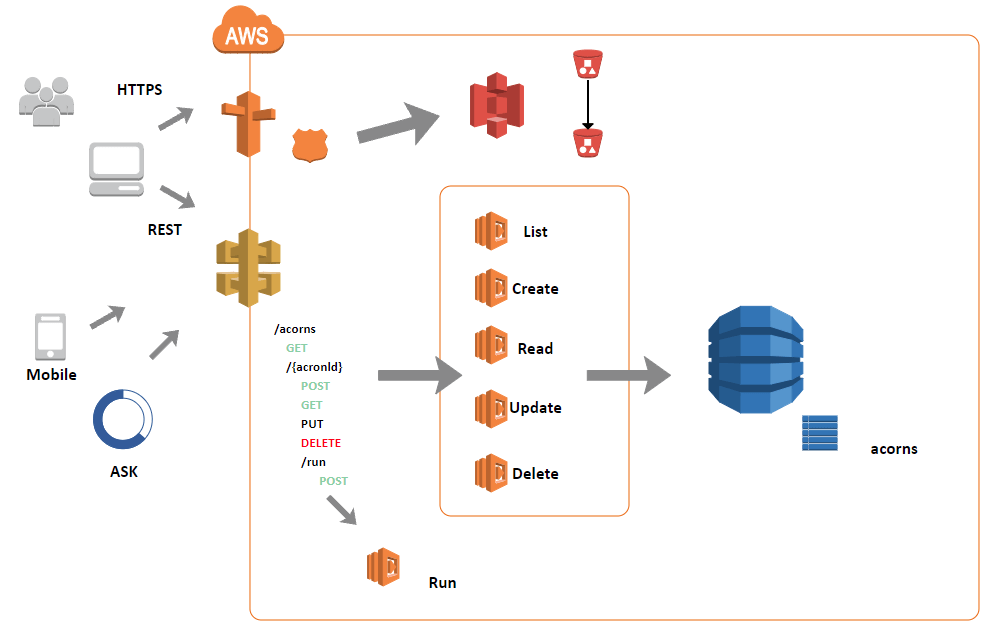
- Identify Appropriate Service Boundaries: The first step in implementing microservices is to identify the appropriate boundaries for your services. Each service should be responsible for a specific business capability or a well-defined set of functionalities. This ensures that services are decoupled and can be developed and deployed independently.
Microservices can be organized based on business capabilities, such as customer management, order processing, or inventory management. By identifying these boundaries, you can design services that are focused, cohesive and have clear responsibilities. This enables teams to work on specific services without interfering with other parts of the system.
- Design for Scalability and Resilience: One of the key benefits of microservices architecture is the ability to scale services independently. Each service should be designed to handle its specific demand effectively. This can be achieved by implementing techniques such as load balancing, clustering, and fault tolerance.

Load balancing ensures that requests are distributed evenly across multiple instances of a service, enabling efficient utilization of resources. Clustering allows for horizontal scaling by adding more instances of a service to handle increased traffic. Fault tolerance techniques, such as redundancy and circuit breakers, help ensure that failures in one service do not cascade and impact the entire system.
- Use Lightweight Communication Protocols: Microservices communicate with each other to fulfill business requirements. It's crucial to choose lightweight communication protocols that minimize overhead and latency. RESTful APIs over HTTP or lightweight messaging systems like RabbitMQ are popular choices.

RESTful APIs provide a simple and scalable way to expose the functionalities of a service. By adhering to REST principles, you can design endpoints that are intuitive and follow standard HTTP methods and status codes. Lightweight messaging systems allow for asynchronous communication and can be useful in scenarios where real-time updates or event-driven architectures are required.
- Ensure Data Consistency and Availability: Maintaining data consistency across microservices can be challenging. As data is distributed across services, it's important to carefully consider how data will be shared and synchronized between services. Implementing techniques such as event sourcing, eventual consistency, and distributed transactions can help address these challenges.
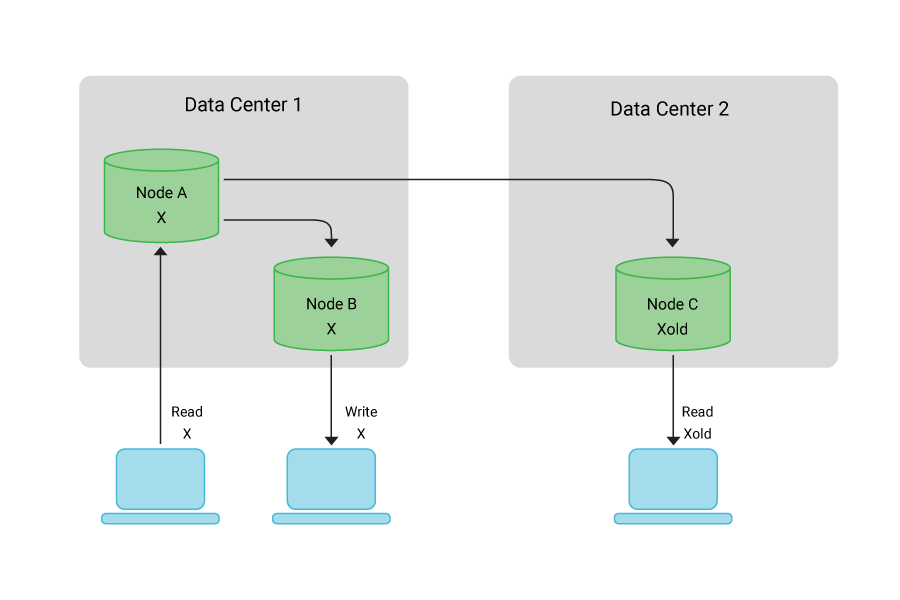
Event sourcing involves capturing and storing events that represent changes to data over time. By replaying these events, services can reconstruct the current state of data. Event-driven architectures can help ensure data consistency and provide an audit trail of changes. Eventual consistency acknowledges that different services may have different views of data at a given point in time, but over time, they converge to a consistent state.
- Implement Robust Service Discovery and Configuration: As the number of microservices grows, it becomes essential to have a robust service discovery mechanism. Services need to be able to locate and communicate with each other dynamically. Implementing a service registry, such as Consul or Eureka, allows services to register themselves and discover other services.

Service registries maintain an up-to-date list of available services, including their locations and metadata. Services can query the registry to discover other services they need to interact with. Additionally, a centralized configuration management system, such as Spring Cloud Config, can simplify managing configurations across services. It ensures that services can dynamically retrieve their configurations without requiring redeployment.
- Continuous Integration and Deployment: To fully realize the benefits of microservices, it's crucial to implement a robust CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline. This ensures that each service can be developed, tested, and deployed independently, minimizing downtime and enabling rapid iteration.

A CI/CD pipeline automates the process of building, testing, and deploying services. It involves using tools like Git for version control, automated testing frameworks, and deployment automation tools such as Jenkins or GitLab CI. Each service should have its own pipeline, allowing teams to independently test and release their services.
- Monitoring and Observability: Monitoring and observability are critical for effectively managing microservices. Implementing centralized logging, distributed tracing, and metrics collection allows for efficient debugging, performance optimization, and proactive issue detection.
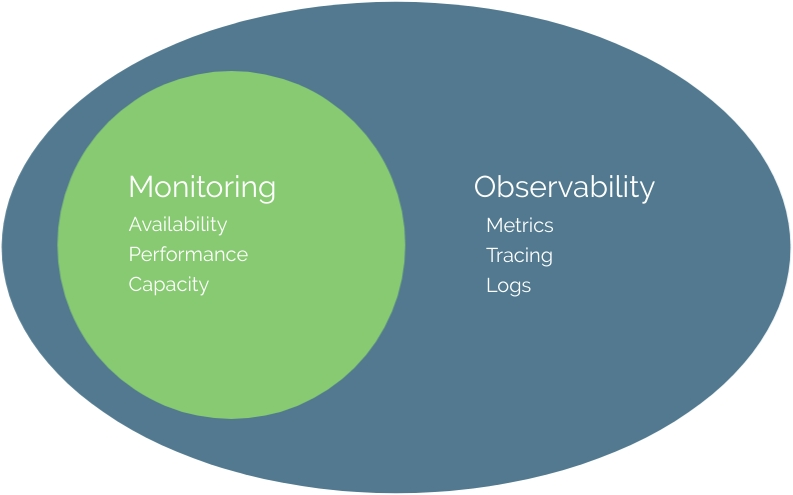
Centralized logging aggregates logs from various services into a single location, enabling easier troubleshooting and analysis. Distributed tracing provides visibility into requests as they flow through multiple services, helping identify performance bottlenecks and latency issues. Metrics collection allows for tracking key performance indicators and identifying trends or anomalies.
Is It Really Worth It?
Implementing microservices can bring several advantages, but it's important to consider the trade-offs:
a. Scalability and Flexibility: Microservices allow for independent scaling and deployment, making it easier to handle increased demand and introduce new features.
b. Team Autonomy: Microservices enable multiple teams to work independently on different services, promoting faster development and flexibility.
c. Resilience: Microservices architecture provides fault isolation, reducing the impact of failures on the entire system.
d. Complexity and Overhead: Implementing microservices introduces additional complexity in terms of service orchestration, data consistency, and communication overhead.
e. Operational Complexity: Managing a distributed system of microservices requires additional effort in monitoring, deployment, and infrastructure management.
Ultimately, the decision to implement microservices depends on the specific needs and requirements of your application. While they offer scalability, flexibility, and other benefits, they also introduce additional complexity. It's important to carefully evaluate the trade-offs and consider the resources, skills, and infrastructure required to implement and maintain a microservices architecture.
Conclusion
Implementing microservices requires thoughtful planning and consideration. By identifying appropriate service boundaries, designing for scalability and resilience, implementing robust communication and deployment mechanisms, and ensuring monitoring and observability, you can harness the benefits of microservices architecture. However, it's crucial to weigh the trade-offs and consider the complexity and operational overhead that comes with microservices. With the right planning, implementation, and resources, microservices can be a powerful architectural approach for building scalable, flexible, and resilient systems.
By understanding and applying the best practices for microservices implementation, such as identifying service boundaries, designing for scalability and resilience, using lightweight communication protocols, ensuring data consistency and availability, implementing robust service discovery and configuration, adopting continuous integration and deployment practices, and prioritizing monitoring and observability, you can overcome the challenges and unlock the benefits of microservices.
While implementing microservices does introduce complexity and operational overhead, the advantages they provide often outweigh the challenges. Microservices offer scalability, flexibility, resilience, and team autonomy, enabling independent development and deployment of services. However, it's important to assess your application's specific needs, the capabilities of your team, and the available infrastructure before deciding to adopt microservices.
In conclusion, implementing microservices requires careful planning, architectural considerations, and a commitment to effective development and deployment practices. When implemented correctly, microservices can unlock the potential for scalable, flexible, and resilient systems. By understanding the best practices and evaluating the worth of implementing microservices based on your project's requirements, you can make an informed decision and leverage this architectural approach to drive the success of your web applications.
